Discover essential information on STD symptoms, including common signs in men and women, when to get STD testing, and tips for preventing STDs. Stay informed and protect your sexual health with expert insights.
Introduction
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), also known as sexually transmitted infections (STIs), are a significant global health concern affecting millions each year. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), there were an estimated 374 million new infections in 2020 alone from just four curable STIs: chlamydia (129 million), gonorrhea (82 million), syphilis (7.1 million), and trichomoniasis (156 million). While more recent data from 2024 indicates over 2.2 million reported cases in the United States, highlighting a persistent rise compared to a decade ago, these numbers underscore the urgency of awareness.
STDs are infections passed primarily through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex, and can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites. They don’t discriminate—anyone who is sexually active can be at risk, regardless of age, gender, or orientation.
Recognizing STD symptoms early is crucial because many infections are asymptomatic, meaning they show no obvious signs, allowing them to spread unknowingly and lead to severe complications like infertility, chronic pain, or even life-threatening conditions such as cancer or HIV-related illnesses. For instance, in my experience as a board-certified nurse working in sexual health clinics, I’ve encountered anonymized cases where young adults dismissed mild discomfort as “nothing serious,” only to later face preventable issues like pelvic inflammatory disease in women or epididymitis in men. Early detection through STD testing can prevent these outcomes, reduce transmission, and improve overall well-being.
This comprehensive guide will help you understand common STD symptoms, with a focus on signs in men and women. We’ll explore major STDs and their manifestations, general indicators that warrant testing, strategies for preventing STDs, available treatments, and debunk common myths. By the end, you’ll be equipped with knowledge to make informed decisions about your health. Remember, this information draws from reliable sources like the CDC and WHO, but it’s not a substitute for professional medical advice—always consult a healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
Start Your Test Today For Your Peace Of Mind


Common STDs and Their Symptoms
Understanding specific STD symptoms is key to early intervention. Below, we cover seven major STDs, highlighting symptoms in men and women, incubation periods (the time from exposure to symptom onset), and the prevalence of asymptomatic cases. Data is based on expert reviews from sources like the CDC and peer-reviewed journals.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia, caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis, is one of the most common STDs, especially among young people. Symptoms often appear 1-3 weeks after exposure, but up to 70-90% of cases in women and 50% in men are asymptomatic.
- STD signs in women: Abnormal vaginal discharge, burning during urination, lower abdominal pain, or bleeding between periods.
- STD signs in men: Discharge from the penis, burning sensation while urinating, or testicular pain.
If untreated, it can lead to infertility. An anonymized case from clinic experience: A 25-year-old woman presented with mild pelvic pain, initially mistaken for a UTI, but testing revealed chlamydia that had progressed silently.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea, from Neisseria gonorrhoeae, typically shows symptoms within 2-14 days. About 50% of women and 10% of men may be asymptomatic.
- STD signs in women: Increased vaginal discharge, painful urination, vaginal bleeding between periods, or pelvic pain.
- STD signs in men: Penile discharge (often white, yellow, or green), burning during urination, or swollen testicles.
Complications include disseminated infection. In practice, I’ve seen men delay seeking help due to embarrassment, worsening the condition.
Syphilis
Syphilis, caused by Treponema pallidum, progresses in stages with an incubation of 10-90 days for the primary stage. Many cases are asymptomatic in later stages.
- Common STD symptoms: Primary: Painless sore (chancre) on genitals, mouth, or rectum. Secondary: Rash, fever, swollen lymph nodes. Tertiary: Severe organ damage if untreated.
- Differences: Symptoms are similar in men and women, but women may experience more internal sores.
A case study from medical literature highlights how early sores are often ignored, leading to spread.
Genital Herpes (HSV)
Herpes simplex virus causes lifelong infections, with symptoms appearing 2-12 days post-exposure. Most are asymptomatic or mild.
- STD signs in women and men: Painful blisters or sores on genitals, buttocks, or mouth; flu-like symptoms during outbreaks.
- Gender note: Women may have more frequent outbreaks due to hormonal factors.
Recurrences are common, as seen in patients managing stress-triggered flares.
Start Your Test Today For Your Peace Of Mind
HIV
HIV attacks the immune system, with acute symptoms 2-4 weeks after exposure resembling flu. Many remain asymptomatic for years.
- Common signs: Fever, rash, sore throat, fatigue, swollen glands.
- No major gender differences in early symptoms, but women may face higher risks of transmission during certain menstrual phases.
Early antiretroviral treatment is vital, transforming HIV into a manageable condition.
HPV (Human Papillomavirus)
HPV often has no symptoms, with warts appearing weeks to months later. Most infections clear naturally, but persistent ones cause cancer.
- STD signs in women: Genital warts, abnormal Pap smears leading to cervical cancer.
- STD signs in men: Warts on penis, scrotum, or anus.
Asymptomatic in 90% of cases.
Trichomoniasis
Caused by a parasite, symptoms appear 5-28 days post-exposure, with 70% asymptomatic.
- STD signs in women: Frothy, odorous vaginal discharge; itching, soreness, pain during sex or urination.
- STD signs in men: Mild discharge, irritation inside penis, burning after urination.
Often overlooked in men.
Start Your Test Today For Your Peace Of Mind
Start Your Test Today For Your Peace Of Mind
General Signs and When to Get Tested
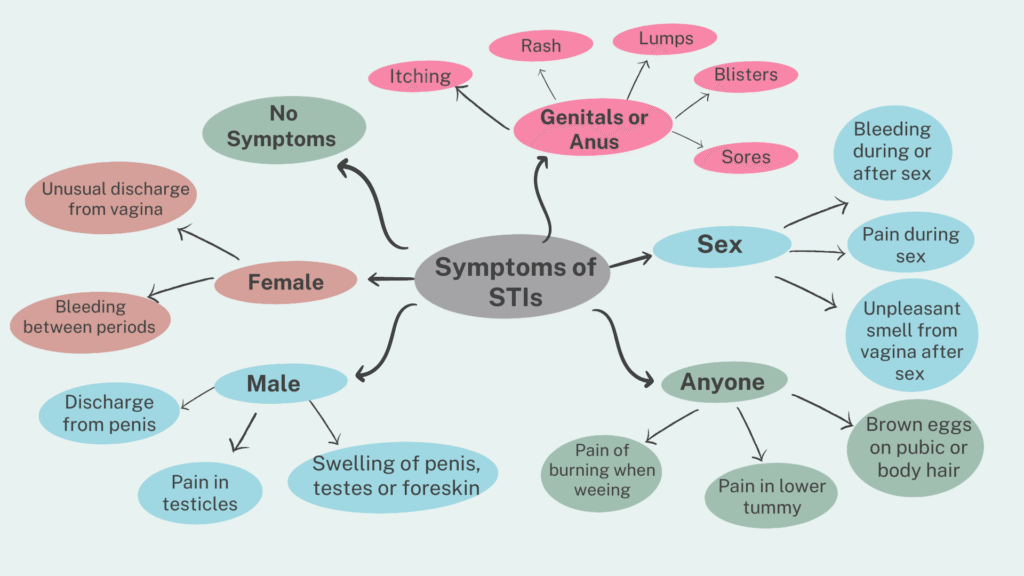
Many STD symptoms overlap, making self-diagnosis tricky. Common indicators include unusual genital discharge, sores or bumps, painful urination, itching, rashes, swollen lymph nodes, lower abdominal pain, or unexplained fatigue. These can mimic other conditions like UTIs or yeast infections, so professional evaluation is essential.
Factors like age and gender influence presentation. Younger individuals (15-24) account for half of new STD cases, often due to asymptomatic infections. STD signs in women might involve vaginal changes or pelvic pain, increasing risks of complications like infertility, while STD signs in men often include penile discharge or testicular issues. Pregnant women face additional risks, such as congenital infections.
STD testing is recommended if you experience any symptoms, have a new partner, or as routine screening—annually for sexually active individuals under 25, or more frequently for high-risk groups like MSM or those with multiple partners. Tests are simple: urine samples, swabs, or blood draws. The CDC advises screening all pregnant women and treating promptly to protect the fetus. In clinic scenarios, I’ve advised patients who felt “fine” but tested positive, preventing further spread.
Don’t wait for symptoms; regular STD testing empowers proactive health management.
Start Your Test Today For Your Peace Of Mind
Prevention, Treatment, and Myths
Preventing STDs starts with safe practices: Consistent condom use, dental dams for oral sex, and open communication with partners. Vaccines are available for HPV (Gardasil) and hepatitis B, significantly reducing risks. Limit partners, get tested together, and avoid sex during outbreaks.
Treatment varies: Bacterial STDs like chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis respond to antibiotics. Viral ones like herpes and HIV are managed with antivirals to control symptoms and transmission. Parasitic infections like trichomoniasis are cured with medications. Early treatment prevents complications, but follow-up testing ensures clearance.
Common myths persist, fueling stigma:
- Myth: Birth control protects against STDs. Debunked: Only barrier methods like condoms do; hormonal birth control prevents pregnancy but not infections.
- Myth: You can’t get STDs from oral sex. False: Many, like herpes and gonorrhea, transmit orally.
- Myth: STDs always show symptoms. Reality: Most are asymptomatic, necessitating regular testing.
Education dispels these, promoting healthier choices.
Conclusion
In summary, recognizing STD symptoms—such as discharge, sores, or pain—early can save lives and prevent spread. We’ve covered common STD symptoms in major infections, general signs prompting STD testing, and strategies for preventing STDs through safe sex and vaccination. Remember, asymptomatic cases are common, so routine checks are vital.
If you notice any signs or are at risk, seek help immediately. Resources like local clinics or hotlines can guide you. Empower yourself with knowledge, but prioritize professional care.
Schedule your STD testing today—visityour nearest lab or your healthcare provider to stay healthy and informed.
Start Your Test Today For Your Peace Of Mind
References
- Mayo Clinic. (2023). Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) – Symptoms and causes. Link
- WHO. (2025). Sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Link
- CDC. (2025). Sexually Transmitted Infections Surveillance, 2024 (Provisional). Link
- JAMA. (2022). Diagnosis and Treatment of Sexually Transmitted Infections: A Review. Link
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Gonorrhea – Symptoms and causes. Link
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Chlamydia trachomatis – Symptoms and causes. Link
- Mayo Clinic. (2025). Trichomoniasis – Symptoms & causes. Link
- Planned Parenthood. (n.d.). What Are STDs? Link
- Teen Vogue. (2016). 10 Myths About STDs That You Should Stop Believing. Link
- The Lancet. (2025). Early detection of sexually transmitted infections from skin lesions. Link
Start Your Test Today For Your Peace Of Mind
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and not a substitute for professional medical advice.